ICP Furnace Showing 80% Limit Fault
Most gas furnaces have several safety limits, main limits, roll-outs, 80%’s will have a DSS (Daft Safety Switch) These safety

VRF Quality Assurance Manager
Gulf Coast District
When troubleshooting any issue, it is always best to start with the most probable cause and work your way to the less likely possibilities. In this article, I will cover some of the basics of why systems freeze up during cooling mode. It might seem like HVAC 101 to some, but for the new talent coming into our trade, this knowledge can be invaluable.
It is important to understand that refrigerant pressure and temperature are relative. If the pressure drops, then the temperature falls accordingly. If the temperature falls below freezing, then available moisture in the air will turn to frost and eventually ice. This process usually begins just past the metering device. When left unchecked, it can work its way across the coil and back to the compressor.
A blower motor must draw air in to move it properly. Low airflow because of a dirty filter can reduce capacity and cause a system to freeze. Closed supply vents on a system can also cause airflow to slow down through the indoor coil. However, these may not be the only issues. Make sure to inspect the entire system thoroughly for other potential problems.
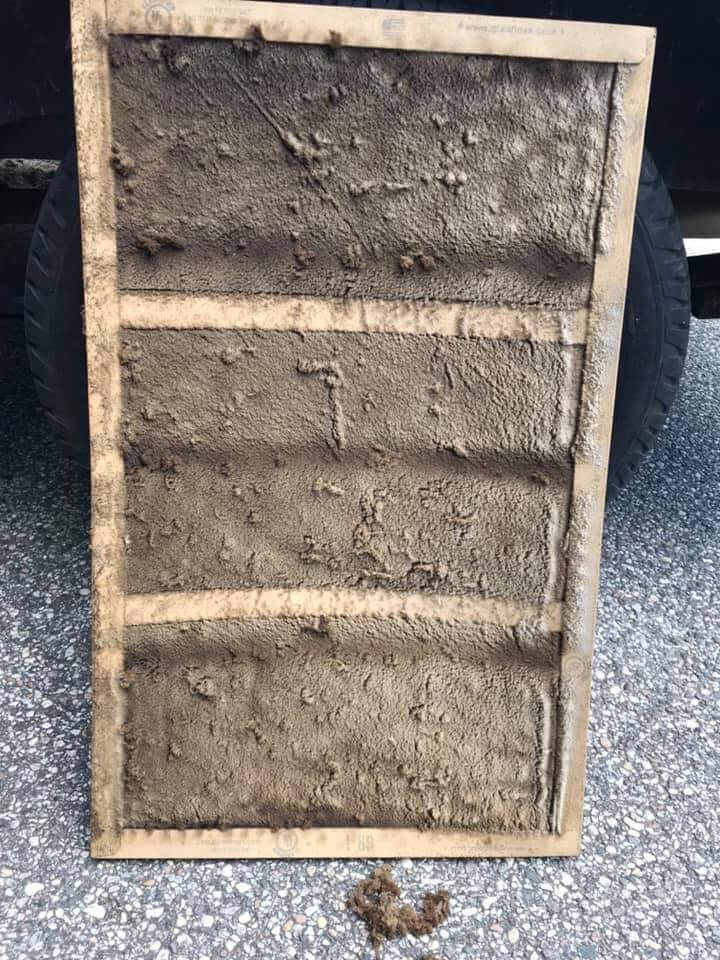
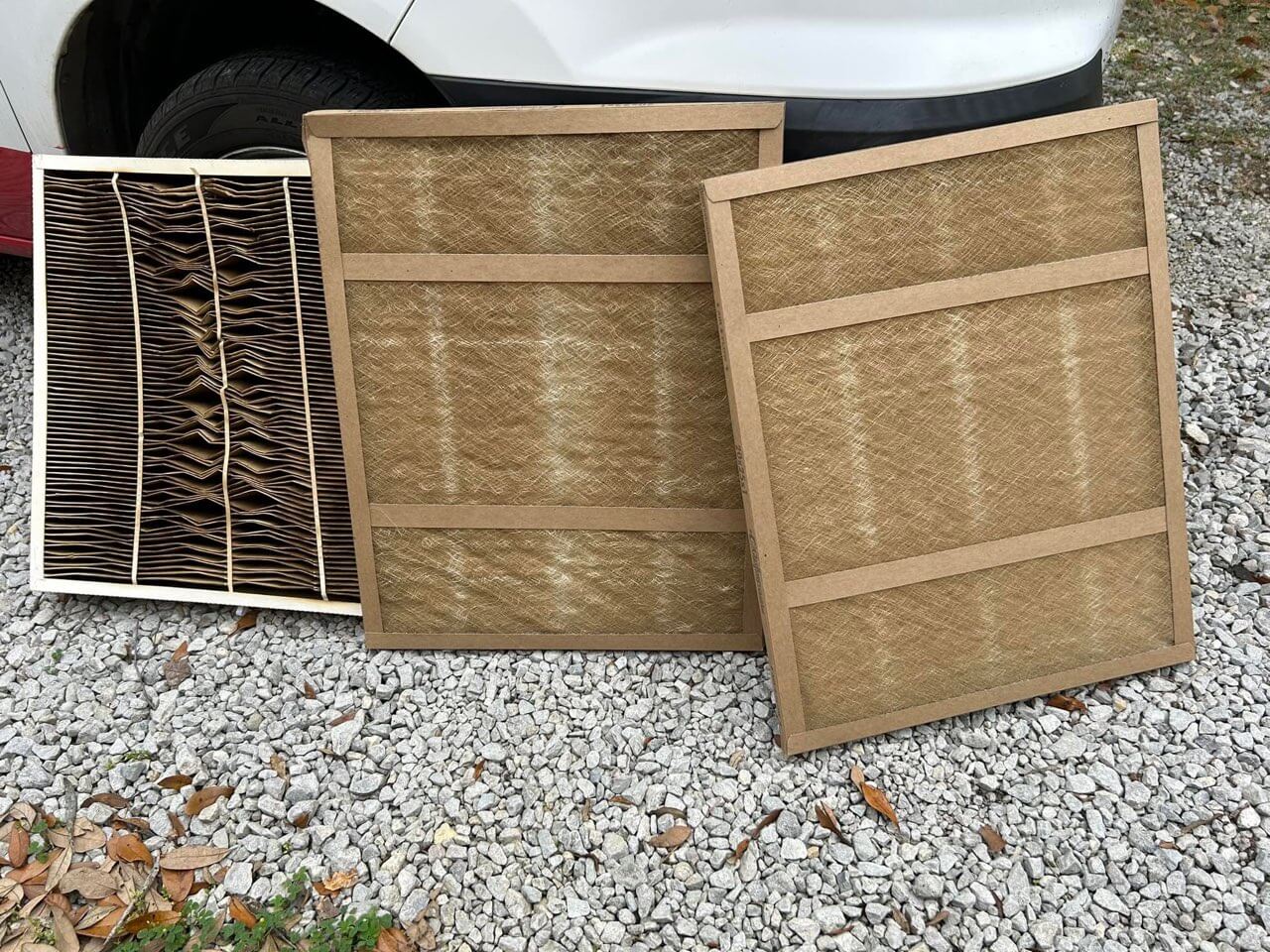


Remind Your Customers to Change Their Filters Regularly. Photos Courtesy of Josh Petty
While checking the filter, take measurements to know if the equipment has enough return air. A good rule is 2 cfm (cubic feet per minute) of air per square inch. Your local and state codes may vary. Most conventional systems are designed to deliver 350-400 cfm per ton.
For example: A 3-ton system moving 400 cfm per ton provides 1200 cfm and requires 600 square inches of return. For this system, a 20×30 return air opening is ideal. Ductulators, sizing charts, and apps are handy tools for verifying the proper size of ductwork.
If it is within line of sight when checking the filter, take note of accumulation or damage. If it is not visible from the filter location, put forth the effort to visually inspect the coil. Knowing the condition will assist in your final diagnosis. If it is too frozen over, you may not be able to tell until thawed.
Does the blower motor run? No… Figure out why and remedy the issue.
Is the outdoor contactor stuck closed? Yes… Replace it.
The points below are common causes for an evaporator coil freezing.
Many applications will have a furnace that is narrower than the evaporator coil. Always follow the guidelines set in the installation manuals. Pay attention to how air flows through the coil. Make sure all areas are getting equal distribution.
Before you check pressures and temperatures, make sure the system is completely thawed. Any ice remaining will affect your readings.
These results may vary based on many other factors in the system.
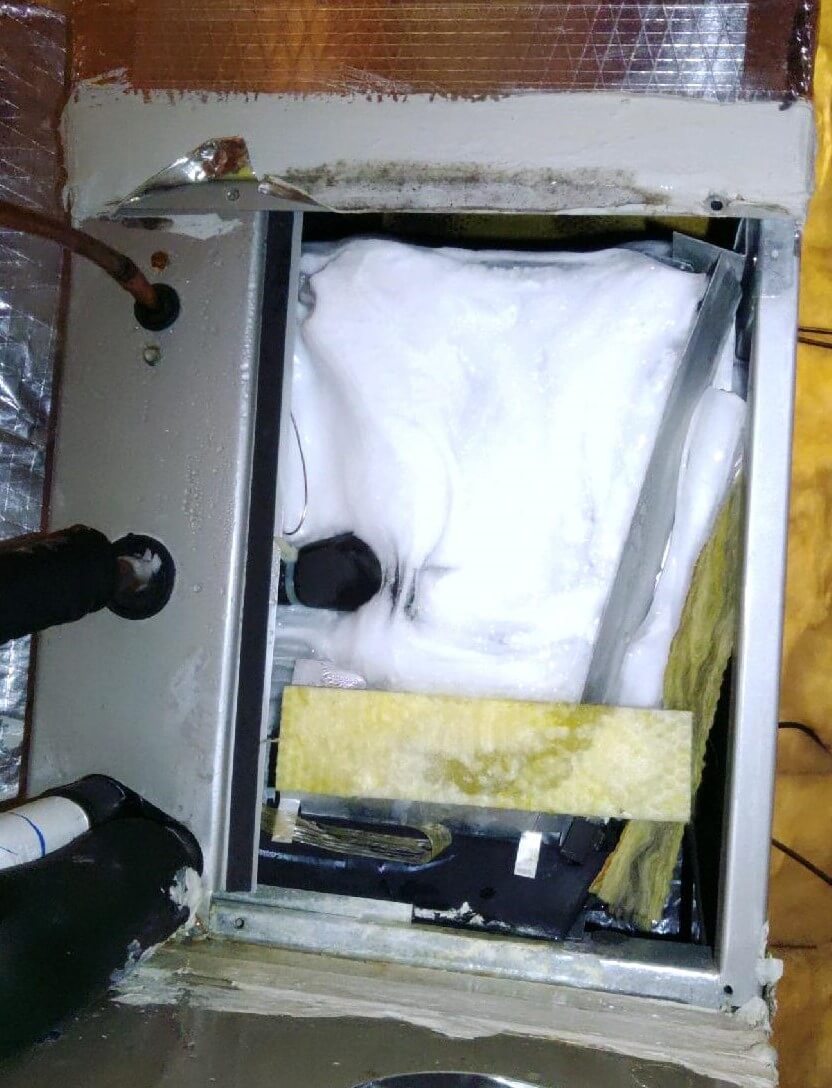
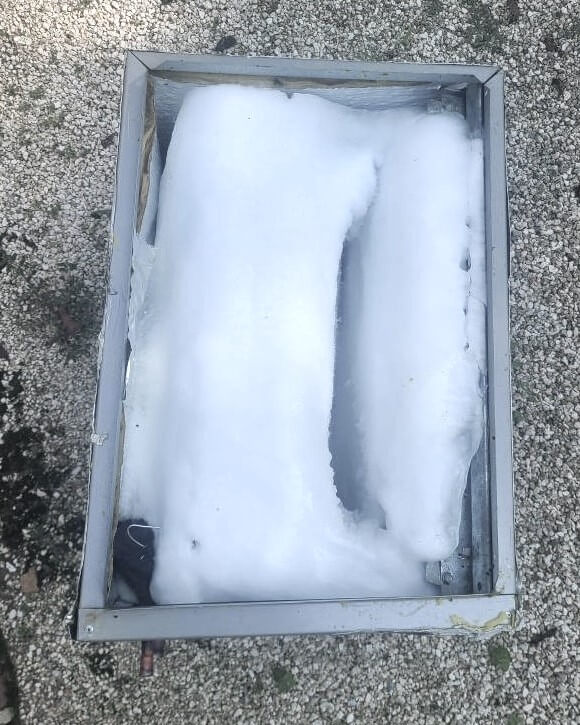


Frozen Coil from Low Refrigerant. Photos Courtesy of Joe Miller
Tech Tip: Never leak search a coil while ice is present. For many leak detectors, the change in atmosphere around thawing Ice can produce a false positive.
Metering devices such as pistons and TXVs are a common place for a restriction. Filter driers can occasionally become clogged. Find this issue by measuring the temperature on both sides of the drier. A temperature drop indicates a restriction. The evaporator coil itself can become restricted. Diagnose by eliminating air flow and watching for irregular freezing patterns in the capillary tubes and individual sections of the coil.
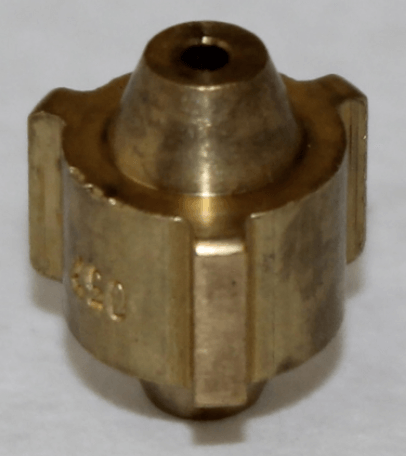
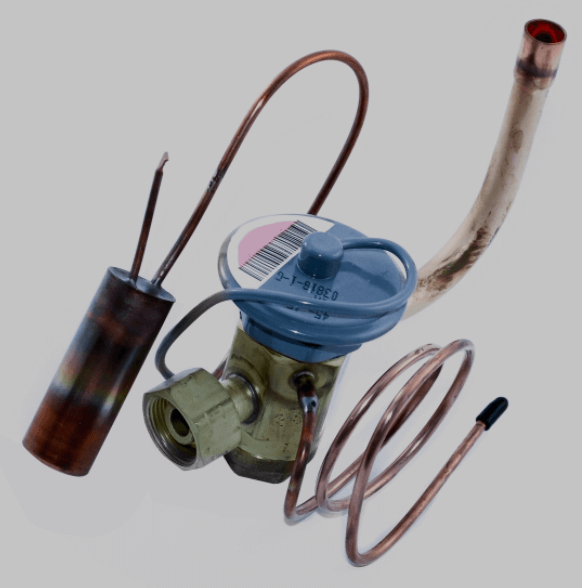



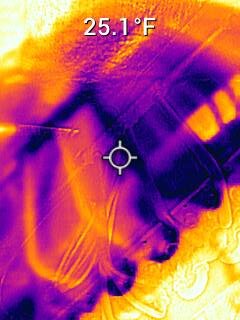
A severe kink in a line can cause refrigerant flash and a significant drop in pressure and temperature. Sometimes, it may be necessary to read temperatures at multiple points across the lines to find this issue.
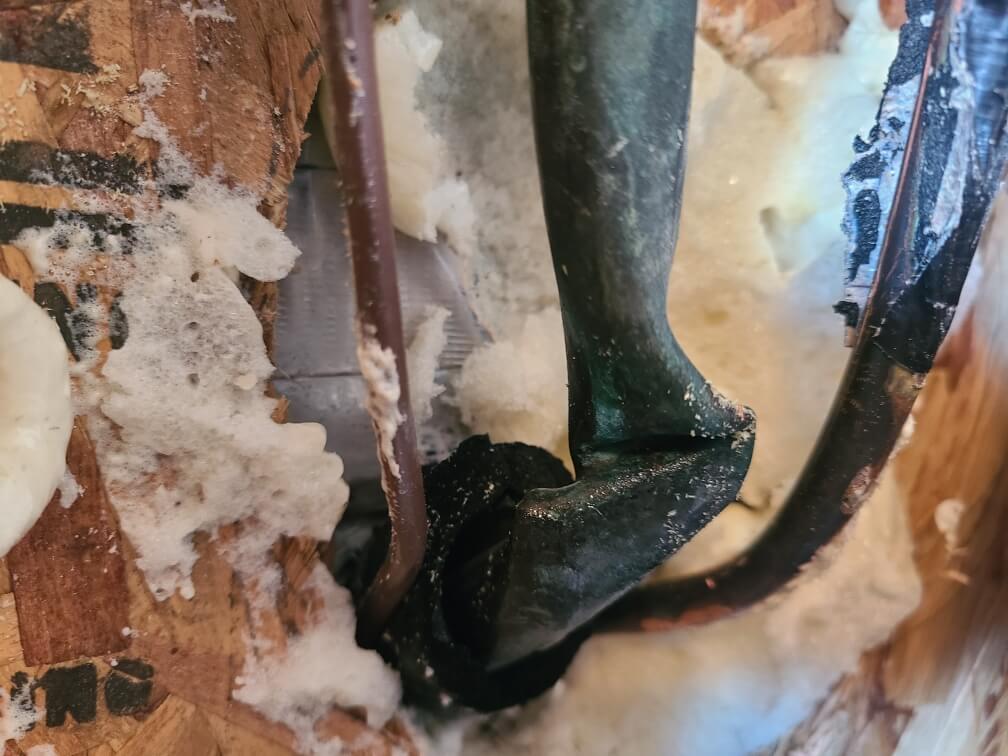

In applications such as server rooms, systems will need to run in the cool mode year-round. If the refrigerant ever falls below freezing, it begins a steady process of forming ice across the evaporator coil. In situations where low ambient cooling is required, it may be necessary to add a freeze-stat to the indoor coil and/or head pressure control at the condenser.
This article has provided a basic understanding of why systems freeze up in cooling mode. Hopefully, it has helped to elaborate on how to understand and diagnose one of the main service calls faced in the HVAC industry.

Disclaimer: The technical statements, information and recommendations contained herein are believed to be accurate as of the date hereof, but Mingledorff’s does not make representations or warranties, express or implied, as to its accuracy, its completeness, or the results to be obtained. The information is being provided for informational purposes only and is intended for use by persons having adequate skill and expertise regarding the proper selection, use and application of the products and recommendations and at their own risk and discretion.
Most gas furnaces have several safety limits, main limits, roll-outs, 80%’s will have a DSS (Daft Safety Switch) These safety
This article is in reference to Residential Heat Pumps. Everyone in the HVAC industry knows that the indoor TXV
Compressors are the heart of the refrigeration system. It creates the pressure difference to move the refrigerant through the system.